What is Diabetes?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), “Diabetes is the condition in which the body does not properly process food for use as energy. Most of the food we eat is turned into glucose, or sugar, for our bodies to use for energy.
“The pancreas, an organ that lies near the stomach, makes a hormone called insulin to help glucose get into the cells of our bodies. When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use its own insulin as well as it should. This causes sugars to build up in your blood. This is why many people refer to diabetes as ‘sugar.’”
Over 30 million people in the United States have diabetes, and in the last 10 years this number has grown by almost 50 percent. There are several types of diabetes, but type 2 diabetes is the most common. Diabetes affects one in four people over the age of 65, and about 90 to 95 percent of the adult cases are type 2 diabetes.
You may hear the term prediabetes (or sometimes called borderline diabetes). This is a condition of high blood sugar, but it is not high enough to be type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes means you may soon have diabetes. It is serious, but a good warning sign to turn things around and prevent yourself from getting diabetes.
Diabetes can lead to other conditions such as:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Blindness
- Kidney failure
- Eye problems
- Foot problems
- Amputations
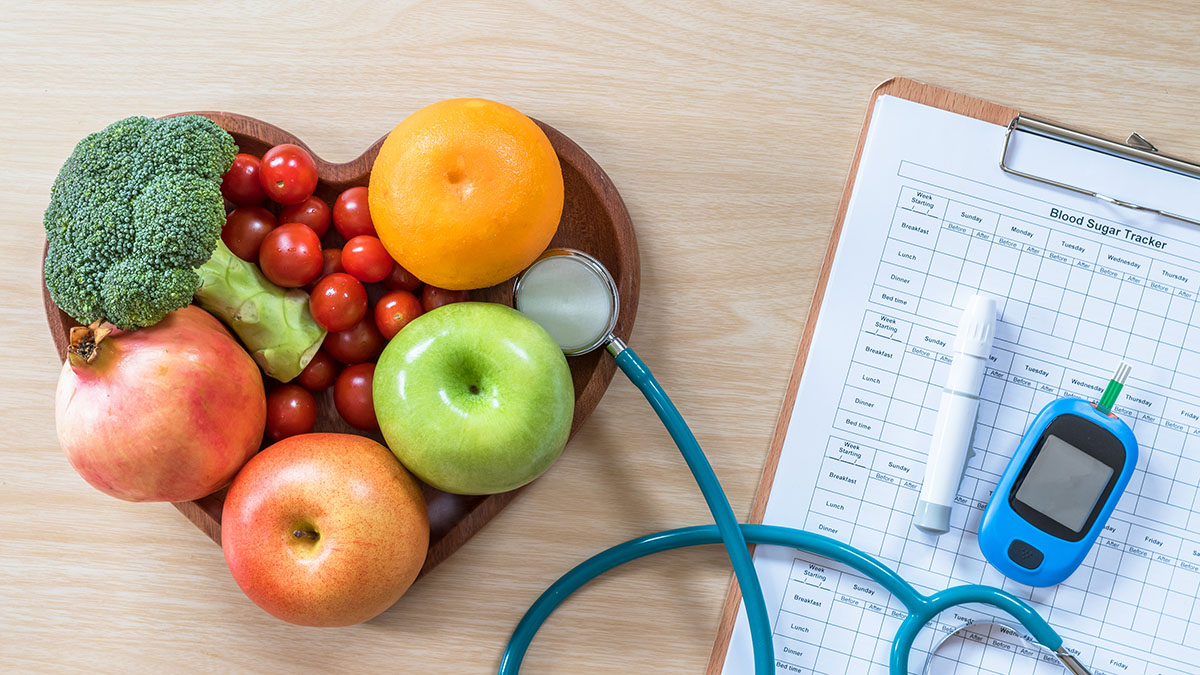
Blood Glucose Testing
A blood glucose test measures the sugar levels in your blood. There are various types of this test. One common test starts with a blood sample. Sometimes your doctor may give you a sugary drink before your blood is taken.
If you already have diabetes, you may be told to monitor your blood sugar yourself. This is done with a home testing kit with which you take a small drop of blood from your finger.
At-home testing helps you figure out when and why your blood sugar numbers might go up or down. Your doctor might even recommend that you do this testing a couple of times a day.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
There are many risk factors for diabetes, and while some of these risks you cannot control, many of them can be managed with lifestyle changes.
Type 2 diabetes risk factors include:
- Having prediabetes,
- Being 45 years or older,
- Being overweight or obese,
- Having high blood pressure,
- Having an unhealthy diet,
- Having a family history of diabetes,
- Having a history of gestational diabetes (high blood sugar during pregnancy), heart disease or stroke,
- Having polycystic ovary syndrome (diagnosed in women with irregular menstrual periods, obesity, excess hair growth),
- Having abnormal cholesterol and triglyceride levels (fats in the blood), or
- Being of African American, Hispanic or Latino, American Indian, Asian American, Pacific islander descent, or being a native of Alaska or Hawaii.
Warning Signs of Diabetes
Of the millions of people who are diagnosed with diabetes each year, almost one in four didn’t even know they had it. It is easy to miss the early symptoms of diabetes, as the signs of it don’t seem too serious. Be alert, and speak to your healthcare professional if you regularly experience any of the symptoms listed above or any of the warning signs below.
These are warning signs of type 2 diabetes:
- Going to the bathroom more than normal,
- Feeling very thirsty,
- Feeling very hungry, even though you eat,
- Unexpected weight loss,
- Fatigue or exhaustion,
- Urinary tract or yeast infections (which can happen especially in women),
- Vision getting worse or blurry vision,
- Cuts, sores or bruises that heal slowly,
- Pain, numbness or tingling in the hands or feet,
- Skin being discolored (in the folds of the neck or on the knuckles of the hands),
- Dry mouth, or
Live Life Well
There is no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed so that you can live a healthy life. There are many things you can do if you are at risk, or to prevent diabetes, such as:
- Lose weight. Weight loss can help improve one’s glucose tolerance.
- Stop smoking. Smoking can increase the risk of the diabetes complications even worse.
- Exercise. Exercise helps your health in many ways, one of which is it uses blood sugar as energy for your muscles. It can also help you lose weight and maintain a healthy weight and exercise lessens stress and may reduce other health risk factors.
- Control your carbohydrate intake. Starchy foods, processed foods, sugars, white flour and breads all break down into sugars in your blood. So, eating a lower carbohydrate diet to reduce sugars in your blood is important.
- Eat more fiber. Fiber can help control blood sugar and contribute to weight loss. Fill your plate with fruits and vegetables and choose whole grain cereals and breads. Check the nutritional information for items that contain at least three grams of fiber per serving.
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water. Sodas and other sweet drinks raise blood sugar.
- Control your alcohol intake. Little or no alcohol makes it easier to control your blood sugar. If you do drink, women should have no more than one drink a day, and men no more than two. If you are monitoring your blood sugar, make sure to check it before you drink.
- Monitor your blood sugar and get regular checkups.
Diabetes Prevention Program:
Are you at risk for diabetes? Now is your time to take action.
By making small changes you can reduce your risk for diabetes and live a happier, healthier life. Change is tough, but we are here to help you.
Jai Medical Systems is now offering a Diabetes Prevention Program to provide you with support and tools to lose weight and reduce the risk of getting diabetes. This program is offered AT NO COST to you.
Call our Customer Service Representatives at 410-433-2200 to learn more about this program.
 Did you know that your IE browser is outdated?
Did you know that your IE browser is outdated?